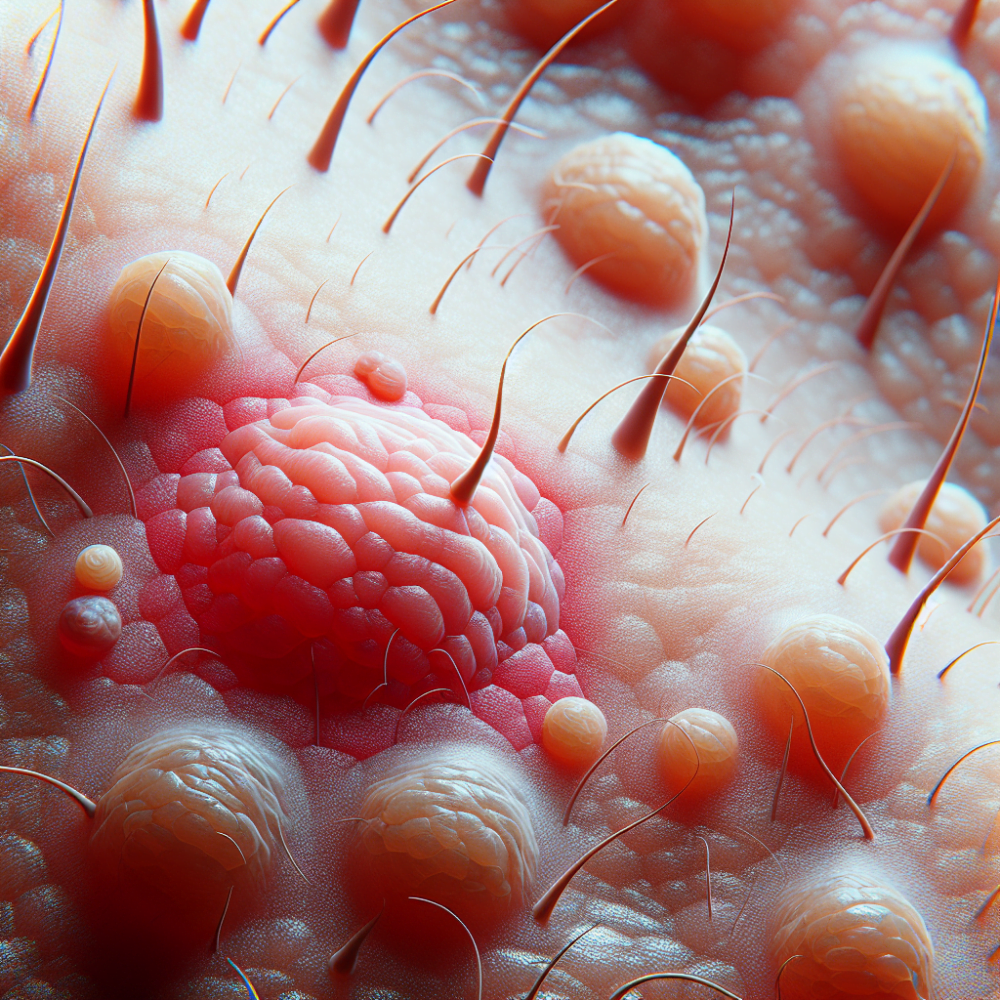
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This irritating and sometimes painful issue occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, often due to bacterial or fungal infections. Despite its prevalence, many individuals struggle to recognize the symptoms and find effective treatments, leading to unnecessary discomfort and potential complications.
Understanding folliculitis is crucial to prevent its occurrence and manage its symptoms effectively. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for folliculitis. From identifying risk factors to exploring both medical and home remedies, readers will gain valuable insights to address this pesky skin problem and maintain healthy, clear skin.
The Basics of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects the hair follicles, which are tiny pockets in the skin from where hair grows. It occurs when these follicles become inflamed or infected, leading to a variety of symptoms such as itching, redness, and the formation of pustules or bumps.
What is a Hair Follicle?
A hair follicle is a tube-like structure within the skin that surrounds the root of a hair. Humans are born with millions of hair follicles all over the body, except on the palms, soles, and lips. These follicles play a crucial role in hair growth and skin health. They are responsible for producing new hairs and helping with wound healing by forming new blood vessels and nervous system cells.
Definition of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is defined as the inflammation of one or more hair follicles, usually due to a bacterial or fungal infection. It can affect any part of the body where hair grows, including the face, scalp, chest, back, arms, and legs. The condition often presents as small, red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps or pustules around the hair follicles.
RELATED: 19 Keto Diet Food List: Essential Foods to Fuel Your Ketogenic Journey
Types and Classifications
Folliculitis can be classified into two main types based on the depth of inflammation:
- Superficial folliculitis: This type involves only a part of the hair follicle and is usually less severe. Examples include:
- Bacterial folliculitis (e.g., staphylococcal folliculitis)
- Hot tub folliculitis (caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria)
- Razor bumps (pseudofolliculitis barbae)
- Pityrosporum folliculitis (caused by yeast)
- Deep folliculitis: This type involves the entire hair follicle and can be more severe, potentially leading to scarring. Examples include:
- Sycosis barbae (barber’s itch)
- Gram-negative folliculitis
- Boils (furuncles) and carbuncles
Folliculitis can also be categorized based on the causative agent:
- Infectious folliculitis: Caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites
- Non-infectious folliculitis: Caused by physical injury, chemical irritation, or certain medications
Understanding the basics of folliculitis, including its definition, the role of hair follicles, and the various types and classifications, is essential for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. While most cases of folliculitis are self-limiting and resolve on their own, some may require medical intervention to prevent complications and promote healing.
Causes and Risk Factors
Folliculitis has a multitude of causes, ranging from bacterial and fungal infections to lifestyle and environmental factors. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for preventing and effectively treating this common skin condition.
Bacterial Culprits
Bacterial infections are the most common cause of folliculitis. Staphylococcus aureus, a bacteria that naturally resides on the skin, is the primary culprit behind superficial bacterial folliculitis. Both methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains of S. aureus can lead to this condition.
Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter, can also cause folliculitis, especially after exposure to contaminated water in hot tubs or swimming pools. This type of folliculitis is often referred to as “hot tub folliculitis” and may occur after prolonged use of oral antibiotics.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, particularly those caused by the Malassezia species, such as Malassezia furfur, can lead to a condition called pityrosporum folliculitis. This type of folliculitis is more common in adolescents due to increased sebaceous gland activity and typically presents in a cape-like distribution over the shoulders, back, and neck. Suspicion of pityrosporum folliculitis should arise when acne fails to respond or worsens after antibiotic treatment.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Several lifestyle and environmental factors can increase the risk of developing folliculitis:
- Frequent shaving, plucking, or waxing of hair
- Wearing tight clothing that traps heat and moisture
- Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids
- Long-term antibiotic therapy
- Exposure to contaminated water in hot tubs, swimming pools, or water slides
- Excessive sweating or hyperhidrosis
- Use of oil-based moisturizers and sunscreens
Certain medical conditions and medications can also predispose individuals to folliculitis. These include:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Immunosuppression or a compromised immune system
- HIV/AIDS, particularly when CD4 counts are low
- Medications such as lithium
Recognizing these risk factors and taking appropriate precautions can help minimize the occurrence of folliculitis. Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding tight clothing, and properly cleaning and maintaining hot tubs and swimming pools are essential steps in preventing this bothersome skin condition.
Identifying Folliculitis



Folliculitis is a common skin condition that can affect individuals of all ages. It occurs when hair follicles become inflamed or infected, leading to a variety of symptoms. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of folliculitis is crucial for prompt treatment and prevention of complications.
Common Symptoms
The most common symptoms of folliculitis include:
- Small red or white pus-filled pimples or bumps around hair follicles
- Itching, burning, or tender skin in the affected area
- Crusty sores that may ooze pus
- Inflamed, red skin surrounding the bumps
In some cases, folliculitis can cause more severe symptoms such as large, painful bumps or masses, fever, and chills. These symptoms may indicate a more serious infection that requires immediate medical attention.
RELATED: Anti Inflammatory Diet: Step-by-Step Guide to Reducing Inflammation
Affected Body Areas
Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where hair follicles are present. However, certain areas are more prone to developing this condition, including:
- Face, particularly the beard area in men (known as pseudofolliculitis barbae or “razor bumps”)
- Scalp
- Arms
- Legs
- Buttocks
- Chest
- Back
Factors such as shaving, tight clothing, excessive sweating, and exposure to hot tubs or swimming pools can increase the risk of developing folliculitis in these areas.
Similar Skin Conditions
Folliculitis can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions that present with similar symptoms. These include:
- Acne vulgaris: This common skin condition causes pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads due to clogged hair follicles. However, acne typically affects the face, chest, and back, while folliculitis can occur on any hair-bearing area of the body.
- Psoriasis: This chronic autoimmune condition causes raised, red, scaly patches on the skin. While some types of psoriasis, such as guttate or pustular psoriasis, may resemble folliculitis, psoriasis generally affects larger areas of the body and is not limited to hair follicles.
- Eczema or dermatitis: These conditions cause red, itchy, and inflamed skin. However, eczema and dermatitis are not typically confined to hair follicles and may present with dry, cracked skin or oozing lesions.
- Fungal infections: Certain fungal infections, such as ringworm or tinea capitis, can cause red, itchy, scaly patches on the skin or scalp. These infections may be mistaken for folliculitis but are caused by fungal organisms rather than bacteria.
If you suspect that you have folliculitis, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can help differentiate folliculitis from other skin conditions and recommend the best course of action to manage your symptoms and prevent complications.
Seeking Medical Help
While mild cases of folliculitis often resolve on their own with proper self-care measures, there are instances when seeking medical help becomes necessary. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms that warrant a visit to a healthcare provider to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
When to Consult a Doctor
If your folliculitis is widespread or the symptoms persist despite self-care measures, it is advisable to make an appointment with your healthcare provider. You may require prescription-strength antibiotics or antifungal medications to effectively control the condition. Seek immediate medical care if you experience signs of a spreading infection, such as:
- Sudden increase in redness or pain
- Fever and chills
- Feeling of being unwell (malaise)
Diagnostic Procedures
In most cases, folliculitis can be diagnosed through a physical examination and a review of your medical history. Your healthcare provider will likely ask about your symptoms, lifestyle habits, and any medications you are currently taking. To confirm the diagnosis or rule out other skin conditions, your healthcare provider may perform the following diagnostic procedures:
- Skin scraping: A small sample of skin cells may be collected and examined under a microscope to identify the presence of yeast or other microorganisms.
- Swab for culture: A sterile cotton swab may be used to collect a sample from the affected area to determine the cause of the infection.
- Skin biopsy: In rare cases, a small skin sample may be taken for further analysis to rule out other conditions.
Possible Complications
Left untreated, severe folliculitis can lead to various complications, including:
- Recurrent or spreading infection
- Permanent scarring
- Temporary skin discoloration (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation)
- Destruction of hair follicles and permanent hair loss
To minimize the risk of complications, it is crucial to seek medical help when necessary and follow the prescribed treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop an individualized approach to manage your folliculitis effectively.
Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of folliculitis depend on the severity and type of the condition. Mild cases often resolve on their own with proper self-care measures, while more severe or persistent cases may require medical intervention. A combination of home remedies, medical treatments, and lifestyle changes can effectively manage folliculitis and prevent recurrence.
Home Remedies
Several home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms of mild folliculitis and promote healing:
- Warm compress: Applying a warm, moist washcloth to the affected area several times a day can help soothe discomfort and encourage drainage of pus-filled bumps.
- Gentle cleansing: Wash the affected skin twice daily with an antibacterial soap and warm water. Use a clean washcloth and towel each time, and avoid sharing these items with others.
- Aloe vera gel: Applying pure aloe vera gel to the affected area may help soothe irritation and promote faster healing due to its antimicrobial properties.
- Essential oils: Diluting tea tree, neem, or grapefruit seed oil with a carrier oil and applying it to the affected area may help combat bacterial and fungal infections. Always perform a patch test before using essential oils on the skin.
Medical Treatments
In more severe or persistent cases of folliculitis, medical treatments may be necessary:
- Topical antibiotics: Creams or gels can be effective in treating mild bacterial folliculitis.
- Oral antibiotics: For widespread or deep folliculitis, oral antibiotics such as dicloxacillin, may be prescribed.
- Antifungal medications: If the folliculitis is caused by a fungal infection, topical or oral antifungal medications may be recommended.
- Drainage: In cases of large boils or carbuncles, a healthcare provider may need to perform a small incision to drain the pus and promote healing.
RELATED: 19 Keto Diet Food List: Essential Foods to Fuel Your Ketogenic Journey
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent folliculitis and manage existing cases:
- Avoid tight clothing: Wear loose, breathable clothing to minimize friction and irritation of the hair follicles.
- Modify shaving habits: For those with pseudofolliculitis barbae or sycosis barbae, consider using an electric razor, shaving less frequently, or applying a shaving gel or cream to reduce irritation.
- Maintain good hygiene: Regularly clean and disinfect items that come into contact with the affected skin, such as towels, washcloths, and razors.
- Avoid hot tubs and swimming pools: If you have a history of hot tub folliculitis, ensure that the chemical levels in the water are properly maintained and shower immediately after using these facilities.
- Manage underlying conditions: If you have diabetes or a weakened immune system, work with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions, as they can increase your risk of developing folliculitis.
By implementing a combination of home remedies, medical treatments, and lifestyle changes, most cases of folliculitis can be effectively managed. If your symptoms persist or worsen despite these measures, consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion
Folliculitis, a common skin issue, can be a real pain for many people. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to dealing with it effectively. From bacterial and fungal infections to lifestyle factors, there are many reasons why this condition might pop up. Knowing when to treat it at home and when to see a doctor can make a big difference in managing the problem and avoiding complications.
Taking care of your skin and making some simple changes in your daily routine can go a long way in preventing folliculitis. Whether it’s using the right skincare products, adjusting your shaving habits, or being careful in hot tubs, these steps can help keep your skin healthy. Remember, while most cases of folliculitis are mild and easy to treat, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if things don’t improve or get worse. With the right approach, you can keep your skin clear and comfortable.